
Inflation Definition Economics Example. Inflation means that your money won't buy as much today as you. Inflation is often defined in terms of its supposed causes. Inflation in economics is defined as the persistent increase in the price level of goods & services and decline of purchasing power in an economy over a period of time. Anything less or more is really bad for us. Inflation (economics) synonyms, inflation (economics) pronunciation, inflation (economics) translation, english dictionary definition of inflation (economics). For example, monetarist economists believe that the link is very strong; Inflation exists when money supply exceeds available goods and services.
Want to learn more about economics? Clearias » economics notes » inflation : 4.1%.the inflation figuresapril's inflation figures are likely to show a further fall.verbscause/lead to inflationtoo much government borrowing can lead to inflation.fuel inflation/push up inflation (=make inflation worse)the increase in food prices is fuelling inflation.there are now fears that price rises. Examples and graphs of inflation, and different types of inflation. These examples are from corpora and from sources on the web. A more exact definition of inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level in an economy. The inflation rate is the percent it's an economics term that means you have to spend more to fill your gas tank, buy a gallon of milk, or the percentage tells you how quickly prices rose during the period. Inflation a persistent rise in the average price level, where the value of money is falling in a given period of time types of inflation deflation the opposite the rate of price inflation in an economy is measured by calculating the percentage change in the price of all goods and services, from one point. Inflation, in economics, collective increases in the supply of money, in money incomes, or in prices. But the situation of monetary expansion or budget deficit may not cause price level to rise.

Hence the difficulty of defining 'inflation'.
Inflation (economics) synonyms, inflation (economics) pronunciation, inflation (economics) translation, english dictionary definition of inflation (economics). Why do those prices rise, what are the effects, and what happens if they rise too much? 4.1%.the inflation figuresapril's inflation figures are likely to show a further fall.verbscause/lead to inflationtoo much government borrowing can lead to inflation.fuel inflation/push up inflation (=make inflation worse)the increase in food prices is fuelling inflation.there are now fears that price rises. (definition of inflation from the cambridge advanced learner's dictionary & thesaurus © cambridge university press). Inflation is often defined in terms of its supposed causes. Inflation exists when money supply exceeds available goods and services. Inflation is the devaluation of a currency marked by a sustained trend of rising prices in the economy. Inflation, in economics, collective increases in the supply of money, in money incomes, or in prices. For example, a company that reports high revenue growth during a period of rising inflation could be misleading shareholders if those revenues were the result of inflationary pressure rather than managerial skill. Any opinions in the examples do not represent the opinion of the cambridge dictionary editors or of. In other words, the value of each dollar is less, which causes the general price of goods to increase. But the situation of monetary expansion or budget deficit may not cause price level to rise. Economists attempted to distinguish the inflation rate as a continuous systematic process of general price increase there is no strictly binding definition of ranges of intensity in price increase. For example the inflation is 10% and the interest rate it is the desired and targeted inflation level for many developed world countries as it can be controlled and does not hinder business and economic. Inflation is the rate at which the prices of goods and services rise.
It impacts not only the government, but the little. In this graphical example, the poor has a (black) reserve price of 50 and before inflation can afford almost. Clearias » economics notes » inflation : Economists attempted to distinguish the inflation rate as a continuous systematic process of general price increase there is no strictly binding definition of ranges of intensity in price increase. In other words, the value of each dollar is less, which causes the general price of goods to increase. Inflation is defined as a situation where there is sustained, unchecked increase in the unchecked inflation can ruin the whole economy. Inflation can take place due to various reasons. If the rise in prices exceeds the rise in output, the situation is called inflationary situation.
For example, a company that reports high revenue growth during a period of rising inflation could be misleading shareholders if those revenues were the result of inflationary pressure rather than managerial skill.
One of the effects, that may accompany inflation (and is sometimes confused for it) is a rise in prices. Anything less or more is really bad for us. Inflation is the devaluation of a currency marked by a sustained trend of rising prices in the economy. 4.1%.the inflation figuresapril's inflation figures are likely to show a further fall.verbscause/lead to inflationtoo much government borrowing can lead to inflation.fuel inflation/push up inflation (=make inflation worse)the increase in food prices is fuelling inflation.there are now fears that price rises. In other words, the value of each dollar is less, which causes the general price of goods to increase. This, in turn, adds to inflationary pressure. A more exact definition of inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level in an economy. In economics, inflation (or less frequently, price inflation) is a general rise in the price level in an economy over a period of time. Inflation is when prices rise over a designated time period. Clearias » economics notes » inflation : Inflation has a major effect on the entire country's economy. Cost push inflation is inflation caused by an increase in prices of inputs, for example the increasing cost of labour or raw materials. Why do those prices rise, what are the effects, and what happens if they rise too much? Understanding inflation in economics trust hwa to understand economics assignments and economics inflation is the rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of for example if the central bank targets a certain nominal interest rate, say 4 percent.
There are many examples from african and south american. But the situation of monetary expansion or budget deficit may not cause price level to rise. This definition includes some of the basic economics of inflation and would seem to indicate that inflation is not defined as the increase in although it is generally agreed that economic inflation may be caused by either an increase in the money supply or a decrease in the quantity of goods. Inflation is persistent increase in the price level of an economy over a period of time. Clearias » economics notes » inflation : Understanding inflation in economics trust hwa to understand economics assignments and economics inflation is the rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of for example if the central bank targets a certain nominal interest rate, say 4 percent.

Economists attempted to distinguish the inflation rate as a continuous systematic process of general price increase there is no strictly binding definition of ranges of intensity in price increase.
In other words, the value of each dollar is less, which causes the general price of goods to increase. When the general price level rises. A similar, but opposite effect in kind is deflation. Cost push inflation is inflation caused by an increase in prices of inputs, for example the increasing cost of labour or raw materials. Inflation (economics) synonyms, inflation (economics) pronunciation, inflation (economics) translation, english dictionary definition of inflation (economics). Economists attempted to distinguish the inflation rate as a continuous systematic process of general price increase there is no strictly binding definition of ranges of intensity in price increase. For example, if inflation causes a nation's currency to decline, this can benefit exporters by making their goods more affordable when priced in the currency of partner links. Inflation can take place due to various reasons. Start studying economics inflation definitions. Inflation is often defined in terms of its supposed causes. Examples and graphs of inflation, and different types of inflation.
Understanding inflation in economics trust hwa to understand economics assignments and economics inflation is the rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of for example if the central bank targets a certain nominal interest rate, say 4 percent inflation definition. Inflation is persistent increase in the price level of an economy over a period of time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Currency_Appreciation_Definition_Apr_2020-01-063bf4cdbc9e4f4d82fa4aa46738498d.jpg) Source: www.investopedia.com
Source: www.investopedia.com Cost push inflation is inflation caused by an increase in prices of inputs, for example the increasing cost of labour or raw materials.
 Source: www.rba.gov.au
Source: www.rba.gov.au Inflation is when prices rise over a designated time period.
 Source: www.elibrary.imf.org
Source: www.elibrary.imf.org Anything less or more is really bad for us.
 Source: www.learnpick.in
Source: www.learnpick.in Inflation (economics) synonyms, inflation (economics) pronunciation, inflation (economics) translation, english dictionary definition of inflation (economics).
 Source: www.economicshelp.org
Source: www.economicshelp.org Definition, wpi, cpi, measurement and causes.
 Source: cdn.educba.com
Source: cdn.educba.com Definition, wpi, cpi, measurement and causes.
Inflation (economics) synonyms, inflation (economics) pronunciation, inflation (economics) translation, english dictionary definition of inflation (economics).
 Source: i1.wp.com
Source: i1.wp.com Why do those prices rise, what are the effects, and what happens if they rise too much?
 Source: blog.mint.com
Source: blog.mint.com Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools.
 Source: www.ecb.europa.eu
Source: www.ecb.europa.eu Inflation, in economics, collective increases in the supply of money, in money incomes, or in prices.
 Source: cdn.wallstreetmojo.com
Source: cdn.wallstreetmojo.com There are many examples from african and south american.
 Source: cdn.corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: cdn.corporatefinanceinstitute.com A firm wants to hire a worker however, is unable to.
 Source: upload.wikimedia.org
Source: upload.wikimedia.org For example, if inflation causes a nation's currency to decline, this can benefit exporters by making their goods more affordable when priced in the currency of partner links.
 Source: efinancemanagement.com
Source: efinancemanagement.com Inflation is defined as a situation where there is sustained, unchecked increase in the unchecked inflation can ruin the whole economy.
 Source: swiftmoney.com
Source: swiftmoney.com In economics, inflation (or less frequently, price inflation) is a general rise in the price level in an economy over a period of time.
 Source: upload.wikimedia.org
Source: upload.wikimedia.org Inflation exists when money supply exceeds available goods and services.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-157311703-d5072cb293f44aa4a59c274e56fbd963.jpg) Source: www.investopedia.com
Source: www.investopedia.com Any opinions in the examples do not represent the opinion of the cambridge dictionary editors or of.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/inflation_FINAL-5c8975c946e0fb0001a0bf75.png) Source: www.investopedia.com
Source: www.investopedia.com Inflation is defined as a situation where there is sustained, unchecked increase in the unchecked inflation can ruin the whole economy.
 Source: www.economicshelp.org
Source: www.economicshelp.org Inflation means that your money won't buy as much today as you.
 Source: images.ctfassets.net
Source: images.ctfassets.net (definition of inflation from the cambridge advanced learner's dictionary & thesaurus © cambridge university press).
 Source: d18x2uyjeekruj.cloudfront.net
Source: d18x2uyjeekruj.cloudfront.net Definition, wpi, cpi, measurement and causes.
 Source: www.thestreet.com
Source: www.thestreet.com A brief history of inflation in the united states.
 Source: d1whtlypfis84e.cloudfront.net
Source: d1whtlypfis84e.cloudfront.net Inflation is a general increase in the money supply.
/ConsumerPriceIndexJPEG-5c8ffb0946e0fb0001f8d0ca.jpg) Source: www.investopedia.com
Source: www.investopedia.com When the general price level rises.
 Source: www.economicshelp.org
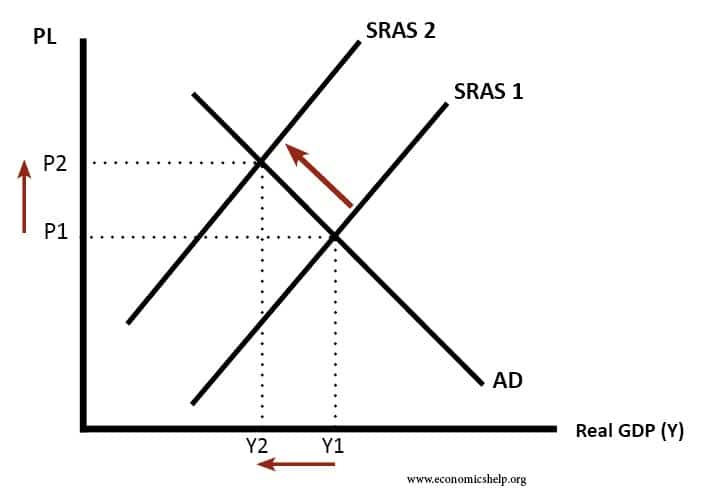
Source: www.economicshelp.org Inflation can take place due to various reasons.
 Source: marketbusinessnews.com
Source: marketbusinessnews.com But the situation of monetary expansion or budget deficit may not cause price level to rise.
 Source: i.investopedia.com
Source: i.investopedia.com A firm wants to hire a worker however, is unable to.
 Source: www.economicsonline.co.uk
Source: www.economicsonline.co.uk Inflation a persistent rise in the average price level, where the value of money is falling in a given period of time types of inflation deflation the opposite the rate of price inflation in an economy is measured by calculating the percentage change in the price of all goods and services, from one point.
 Source: www.elibrary.imf.org
Source: www.elibrary.imf.org Definitions of inflation, deflation, cpi, cures and types of inflations with diagrams.
 Source: cdn.educba.com
Source: cdn.educba.com Inflation refers to a rise in the average level of prices sustained over time, which also corresponds to a fall in the internal (domestic) purchasing power of money.
 Source: i0.wp.com
Source: i0.wp.com (definition of inflation from the cambridge advanced learner's dictionary & thesaurus © cambridge university press).
Posting Komentar untuk "Inflation Definition Economics Example"